Waveguide Loss Factors: Skin Depth, Surface Finish, and Mechanical Alignment
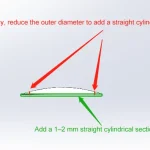
In the world of millimeter-wave and terahertz technology, every decibel counts. You might have the most advanced RF source, but without a perfectly optimized waveguide, your signal could be dissipating as heat before it ever reaches its destination. From microscopic surface textures to the precision of a flange connection, even the smallest imperfection can lead […]
Waveguide Loss Factors: Skin Depth, Surface Finish, and Mechanical Alignment Read More »